VMware Virtual Appliance is a virtual device (Debian Linux with pre-installed Kerio Workspace) can be used in VMware products. http://www.kerio.com/workspace/technical-specifications.
Use an installation package in accordance with the type of your VMware product (see above):
In case of products VMware Server, Workstation and Fusion, download the compressed VMX distribution file (
*.zip), unpack it and open it in the VMware product.You can import a virtual appliance directly to VMware ESX/ESXi from the URL of the OVF file — for example:
http://download.kerio.com/dwn/workspace/kerio-workspace-appliance-1.x.x-1270-linux.ovfVMware ESX/ESXi automatically downloads the OVF configuration file and a corresponding disk image (
.vmdk).
If you import virtual appliance in the OVF format, bear in mind the following specifics:
In the imported virtual appliance, time synchronization between the host and the virtual appliance is disabled. However, Kerio Workspace features a proprietary mechanism for synchronization of time with public Internet time servers. Therefore, it is not necessary to enable synchronization with the host.
Tasks for shutdown or restart of the virtual machine will be set to default values after the import. These values can be set to “hard” shutdown or “hard” reset. However, this may cause loss of data on the virtual appliance. Kerio Workspace VMware Virtual Appliance supports so called Soft Power Operations which allow to shut down or restart hosted operating system properly. Therefore, it is recommended to set shutdown or restart of the hosted operating system as the value.
When you run the virtual computer, Workspace graphical console is displayed. The console is protected by the root password. The password is at first set to: kerio
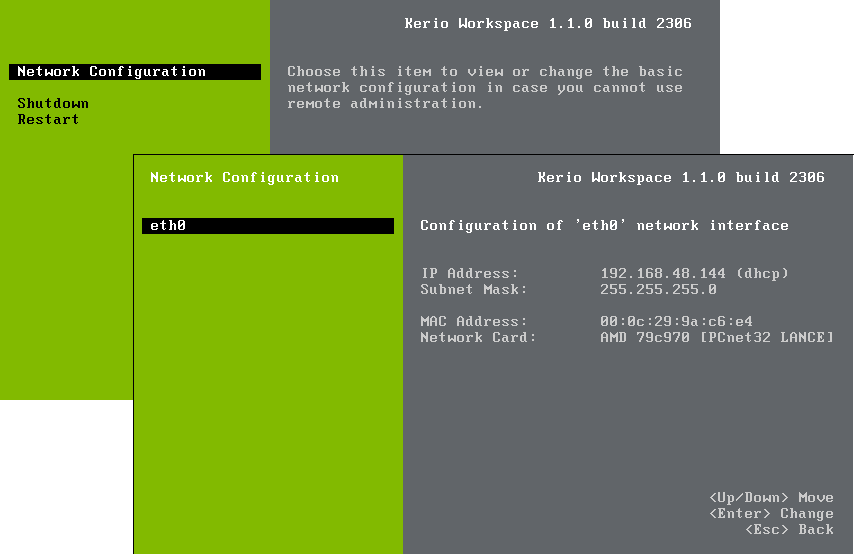
the console allows you to configure the network, restart or shut down the computer (figure 2.1 Console — network configuration).
The network configuration allows you to:
display network adapters — MAC address, adapter name and IP address
configure network adapters
DHCP
static IP address
more static IP addresses
Note
If you use a DHCP service on your network, the server will be assigned an IP address automatically and will connect to the network. If you do not use or do not wish to use DHCP for Kerio Workspace, you have to set the IP address manually.
If the IP address is assigned by the DHCP server, we recommend to reserve an IP address for Workspace so that it will not change.
A terminal is available for product and operating system updates. You can run it by pressing the standard Alt+Fx combination (for example, Alt+F2) for running new console.
If you access the system via shell for the first time, log in as root:
Name: root
Password: kerio
The system invites you to change the password.
VMware Appliance also allows the access via SSH which will be required for update packages uploads.